In today's economy it is imperative that database developers work smarter, not harder, to meet the demands put on them by line of business owners, senior management, and the company as a whole. Due to time, money, and resource limitations it is often no longer feasible to rewrite, re-architect, or even replace databases that are core to running a business as a means of achieving better performance or scalability. Likewise, simply throwing additional computing resources at the problem in an attempt to extend the life of an application or system is often no longer feasible due to capital costs. The only option is to get more out of existing systems with as little effort as possible.
It all circles back to optimization. Performance optimization is a key ingredient in the struggle to stretch an invested IT dollar to its absolute limit. From a productivity perspective, database performance is becoming more critical in everyday business transactions. There is no time to waste on a slow query. Performance optimization problems can occur at any stage of the development lifecycle, so organizations need to take a three step approach to this problem: prevent, find, fix.
IDERA offers database optimization tools for database developers and database administrators to prevent, find, and fix problems that impact performance throughout the system development lifecycle. IDERA tools help database professionals:
- Build high-performing databases
- Assess and optimize the performance of database queries
- Keep poor-performing (and costly) code from reaching production
Database and code optimization tools detect problems earlier, address issues faster, minimize the chance of deploying poor-performing SQL code, and ultimately deliver higher quality solutions. Performance optimization tools can also minimize IT spend on additional hardware to handle peak-load requirements by ensuring the databases are optimized to fully utilize existing IT resources.
Database developers are under increasing pressure to maintain the highest levels of database performance. They must balance customer satisfaction and productivity with rising costs and shrinking budgets. Throwing more hardware or resources at the problem is no longer an option. Neither are outages or delays. Optimization tools such are needed to ensure that poor-performing code never reaches the production environment – where it is significantly more costly to correct bad SQL code.
It is the developer's responsibility to prevent poor-performing SQL code from reaching production in the first place. IDERA DB Optimizer is a SQL profiling and tuning tool that examines SQL queries to uncover inefficiencies and offers alternatives to improve SQL performance and prevent poor-performing SQL from ever reaching the production environment.
SQL queries are the primary mechanism to interact with databases, so developers must ensure that SQL queries perform well. An important method to improve the performance of SQL queries is to use indexes properly to locate data quickly. To create useful indexes, it is essential to understand how databases store data versus what type of data SQL queries need to access.
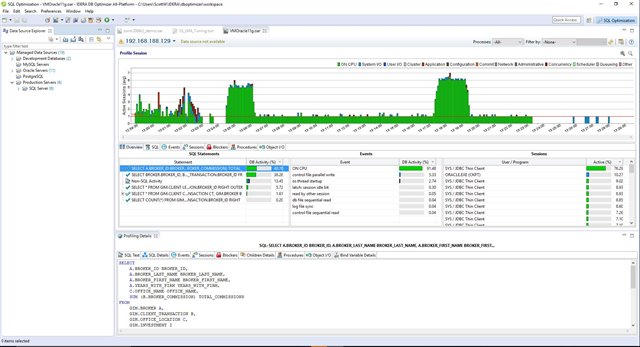
Figure 1: DB Optimizer’s graphical profiling with details on SQL statements, events, and sessions makes it easy to find the SQL that most impacts performance.
Starting with profiling, DB Optimizer can analyze a single SQL statement or an entire database to determine which queries should be focused on for improvement. In some cases these may be long-running queries. In other cases they may be queries that execute repetitively. Both are worth the effort to try and improve overall performance.
Once the problem statements have been identified, DB Optimizer can begin tuning. Tuning is the process of actually making changes: studying a number of different options (known as cases), the "costs" of each option, and implementing the case that provides the best execution plan. Visual SQL tuning refers to parsing a SQL query, analyzing the indexes and constraints on the tables in the SQL query, and displaying the SQL query represented as relational models in diagrams. Visual SQL tuning helps developers to see flaws in designs of schemas (such as Cartesian joins, implied Cartesian joins, and many-to-many relationships). The visual SQL tuning diagram also helps developers to understand the components of the SQL query more quickly, thus accelerating troubleshooting and analysis.
DB Optimizer also provides batch tuning of DML statements, stored routines, and entire SQL files, producing a number of execution plans, displayed on a grid, with detailed statistics for each case. The best case can easily be selected to automatically replace the existing poor-performing SQL statement. Learn more about SQL query tuning and steps to do it efficiently in this infographic.
Learn more about how DB Optimizer can streamline your SQL code performance, and try it for free to test it in your own environment.