InterBase bietet seit “Menschengedenken” die Möglichkeit an, Arrays zu benutzen.
Was sind Arrays?
Arrays sind ein- oder mehr-dimensionale Datenspeicher vom gleichen Typ innerhalb einer Spalte. Diese können bei InterBase mit allen Standard-Datentypen verwendet werden, bis auf BLOBs.
Wann sollte man diese benutzen / wann nicht?
Arrays können recht einfach definiert werden. Dabei sollte man aber beachten, wann man diese einsetzen sollte und wann man das besser sein lässt:
- Die Daten des Arrays sind vom gleichen Typ
- Die Daten des Arrays werden als logische (Daten gehören zusammen) und physikalische (Speicherung in einer Spalte; unter gemeinsamen Transaktionskontrolle) Einheit verwandt.
Vorteile ergeben sich durch die verringerte Last durch die Transaktionskontrolle: Man kann einfach einen Rutsch Daten (ein/mehrdimensional) in ein Arrays innerhalb einer einzelnen Transaktion lesen und speichern. Letzteres ergibt uU deutliche Performancevorteile
Das Anlegen von Arrays geschieht als Erweiterung von CREATE TABLE bzw CREATE DOMAIN:
CREATE TABLE TBL_ARRAY ( ID INTEGER, TICTACTOE BOOLEAN[1:3, 1:3]
<code>);
Hier wird ein Tic Tac Toe Feld in einer Spalte definiert.
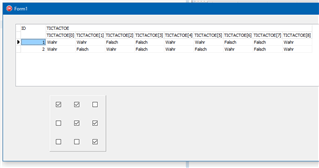
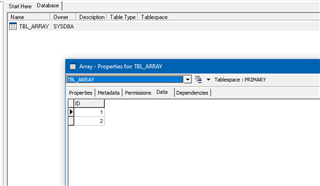
Durch / mit FireDAC sieht das zB in der Delphi IDE so aus:
(Ansicht aus dem Datenexplorer)
Innerhalb einer Anwendung. (Normales DBGrid und 3×3 DBCheckBox)
Zu beachten ist es, daß zuerst die Zeilen/Rows und dann die Spalten/Columns im Array durchlaufen werden. Fortran erwartet zB eine Spalten/Zeilen Ordnung.
Ab Berlin 10.1 wird vom DBGrid auch ein Array richtig dargestellt!
Programmtechnischer Zugriff auf die Array Elemente
Die Array Elemente lassen sich über die 0-basierten Elemente direkt zugreifen. Hier mal alternierend:
Tbl_arrayTable.Edit; Tbl_arrayTable.FieldByName('TICTACTOE[0]').Value := NOT Tbl_arrayTable.FieldByName('TICTACTOE[0]').AsBoolean;
Was gibt es zu beachten?
Die InterBase Console kann Arrays leider nicht anzeigen:
Mein Kollege Stephen Ball hat darüber auch mal ein schönes Video gemacht (in englischer Sprache)