Microsoft SQL Server stores a significant amount of data in the tempdb system database. Consequently, tempdb can fill up quickly when disk space is low, or the maximum size for database growth is small. Also, specific workloads may cause excessive space usage or create contention in tempdb, which can affect performance on the entire server. A whole SQL Server instance can become inoperable due to problems with tempdb. Tempdb is a very critical component of SQL Server. It can be a significant performance pain point if not managed properly. Having a performant tempdb starts with proper configuration and includes consistent baselining and monitoring of tempdb.
There exist many misconceptions and myths about tempdb. Purported best practices are inconsistent at best. It is hard to know which advice to follow when one resource says always to do it one way and another always says to do it the opposite direction. Many times, both resources are correct in certain situations or to a certain degree. Part of the problem is that rarely is there a single right solution to any scenario in Microsoft SQL Server. Unfortunately, many database administrators will assume that because a practice worked for them in one situation that they should do the same method in every case. Clear guidance on best practices for managing tempdb to provide the optimum balance between performance, reliability, and manageability.
The completely free 17-page whitepaper “Demystify Tempdb Performance and Manageability” provides guidance on how to make the right decisions for managing tempdb to help you determine the proper solution for any given scenario. To be able to make these decisions, several concepts must be understood. The whitepaper describes what tempdb is, how to use it, some common significant problems, and how to prevent them. The whitepaper also provides some best practices on configuring and monitoring tempdb. The presented best practices will help to prevent, detect, and mitigate common performance problems. Couple these best practices with an understanding of how tempdb works and the role it plays to guide troubleshooting issues with tempdb.
The author, Robert L. Davis, is a senior database administrator and technical lead at Microsoft. He has over 11 years of experience with SQL Server, including expertise in high availability, disaster recovery, performance tuning, and data architecture. He is a speaker and trainer. He is also a writer for SQL Server Magazine and co-authored “Pro SQL Server 2008 Mirroring” by Apress.
Click here to read the whitepaper.
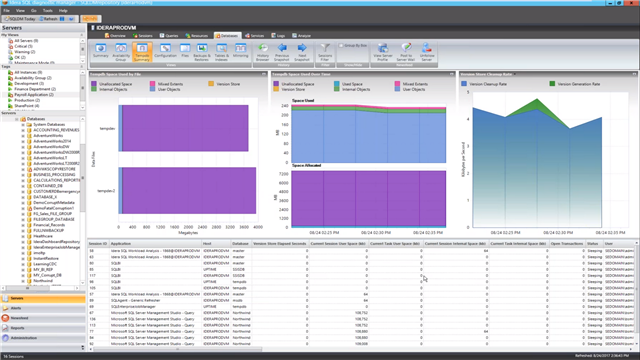
Quickly identify and resolve tempdb performance issues using SQL Diagnostic Manager. View the space, contention, and health of tempdb via a series of charts, views, alerts, and reports that are unique to tempdb. In detail, monitor the file space, version store, sessions space usage, and wait stats for tempdb.
Read the blog post “How to monitor tempdb databases” with SQL Diagnostic Manager and watch the video “Five Key Features of SQL Diagnostic Manager” that includes tempdb monitoring and analysis. Also, download a fully functioning 14-day trial, request a one-on-one demonstration, and request a price quotation.